Compiled trait
Structure of the generated trait#
PHP traits are compiled into corresponding CLR types. The sample below depicts a PHP trait and resulting CLR type decompiled into C# language.
<?php
trait T {
function foo() { return 1; }
// ...
}
[PhpTrait]
[PhpType("T", "index.php")]
public sealed class T<TSelf> where TSelf : class {
// 'TSelf' is type of class that uses this trait.
public T(Context ctx, TSelf @this) { ... }
public long foo() { return 1L; }
// ...
}
Traits are special case of types. The compiler can generate classes with multiple inheritance using traits. The sample below shows a PHP class using a trait and the resulting CLR type decompiled into C# language.
The compiled class then automatically declares all the members of the trait. Their implementation calls the trait members internally.
<?php
class X {
use T;
}
[PhpType("X", "index.php")]
public class X {
private readonly T<X> <>trait_T; // holds instance of the trait
public X(Contex <ctx>) {
this.<>trait_T = new T<X>(<ctx>, this);
}
public virtual long foo() {
return this.<>trait_T.foo();
}
}
Constructors#
The trait constructor is always in the form below:
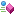
public .ctor(Context ctx, TSelf @this)
The constructor initializes the trait with instance to$thisand current context. This constructor is well known to the compiler and it is used by classes that use the trait.
Attributes#
The type is annotated with [PhpTypeAttribute] and [PhpTraitAttribute]. The attribute contains fully qualified PHP class name and relative file path where it was declared.